NMY51酿酒酵母报告菌株-膜蛋白酵母双杂交系统-BioVector NTCC质粒载体菌种细胞蛋白抗体基因保藏中心
- 价 格:¥19322
- 货 号:NMY51酿酒酵母报告菌株-膜蛋白酵母双杂交系统
- 产 地:北京
- BioVector NTCC典型培养物保藏中心
- 联系人:Dr.Xu, Biovector NTCC Inc.
电话:400-800-2947 工作微信:1843439339 (QQ同号)
邮件:Biovector@163.com
手机:18901268599
地址:北京
- 已注册
NMY51酿酒酵母报告菌株
BioVector NTCC质粒载体菌种细胞蛋白抗体基因保藏中心
NMY51 Yeast reporter strain
MATa his3Δ200 trp1-901 leu2-3,112 ade2
LYS2::(lexAop)4-HIS3 ura3::(lexAop)8-lacZ
ade2::(lexAop)8-ADE2 GAL4
Lyophilized yeast culture
The yeast two-hybrid membrane protein system was developed to identify and characterize
protein-protein interactions between integral membrane proteins, membrane-associated
proteins and soluble proteins in their natural setting.
Unlike the yeast two-hybrid system, there is no need for your bait to be transported to the
nucleus and therefore, interactions between full-length integral membrane proteins can be
readily detected in situ at the cellular membrane.
The yeast two-hybrid membrane protein kit version 3 contains improved vectors which
help you express mammalian integral membrane proteins or membrane-associated proteins
in yeast for screening against cDNA libraries, an expanded manual and a trial size HTX β-
galactosidase assay kit for fast, quantitative determination of β-galactosidase levels in yeast.
Y2H membrane cDNA libraries
The yeast two-hybrid membrane protein system can be used to assay the interaction
between two known proteins or to find novel interaction partners of a protein of interest by
screening cDNA libraries.
How does the Y2H membrane protein system work?
The Y2H membrane protein system takes advantage of a classical protein complementation
assay, the split-ubiquitin system (Johnsson and Varshavsky, 1994), to detect the interaction
of two heterologously expressed fusion proteins in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In
contrast to the most popular yeast based screening system, the yeast two-hybrid system
(Fields and Song, 1989), there is no requirement for the interacting proteins to be located in
the nucleus. Therefore, the Y2H membrane protein system allows investigation of proteinprotein
interactions involving full-length integral membrane proteins or membrane-associated
proteins in their natural setting at the cellular membrane.
Advantages of the Y2H membrane protein system are:
Full-length proteins can be assayed
Interactions are detected at the cellular membrane
Interactions involving integral membrane proteins, membrane-associated proteins and
soluble proteins can be detected
Post-translational modifications such as glycosylation are preserved
2 How to carry out a Y2H membrane screen
YEAST TWO HYBRID MEMBRANE
The split-ubiquitin mechanism Target
The Y2H membrane protein system is based on the reconstitution of ubiquitin, a small and
highly conserved protein which tags other proteins for degradation (Hershko, 2005; Mayer,
2000). When an intracellular protein is destined for degradation, a series of enzymatic
reactions covalently attaches a chain of ubiquitin molecules to this protein (Figure 1A). The
poly-ubiquitin tagged protein is then transported to the 26S proteasome, where it is degraded
(Figure 1B). To recycle the ubiquitin, the cell has evolved a mechanism to cleave the polyubiquitin
chain off the target protein. This process is mediated by so-called ubiquitin specific
proteases (UBPs). The UBPs specifically recognize intact, folded ubiquitin and cleave the
polypeptide chain after the last residues of ubiquitin (a Gly-Gly motif). Free monomeric ubiquitin
is thus released back into the cytosol, whereas the target protein is degraded.
The Yeast Two-Hybrid Membrane Protein System
The Y2H membrane (Stagljar et al., 1998; Thaminy et al., 2003) system takes advantage of
the split-ubiquitin mechanism to measure the interaction between an integral membrane
protein and its interaction partners (either integral membrane proteins or soluble proteins).
As the interaction is detected in situ at the membrane, the assay represents a more
physiological situation than a conventional yeast two-hybrid assay, where only subdomains
of integral membrane proteins can be assayed and the interaction takes place in the nucleus.
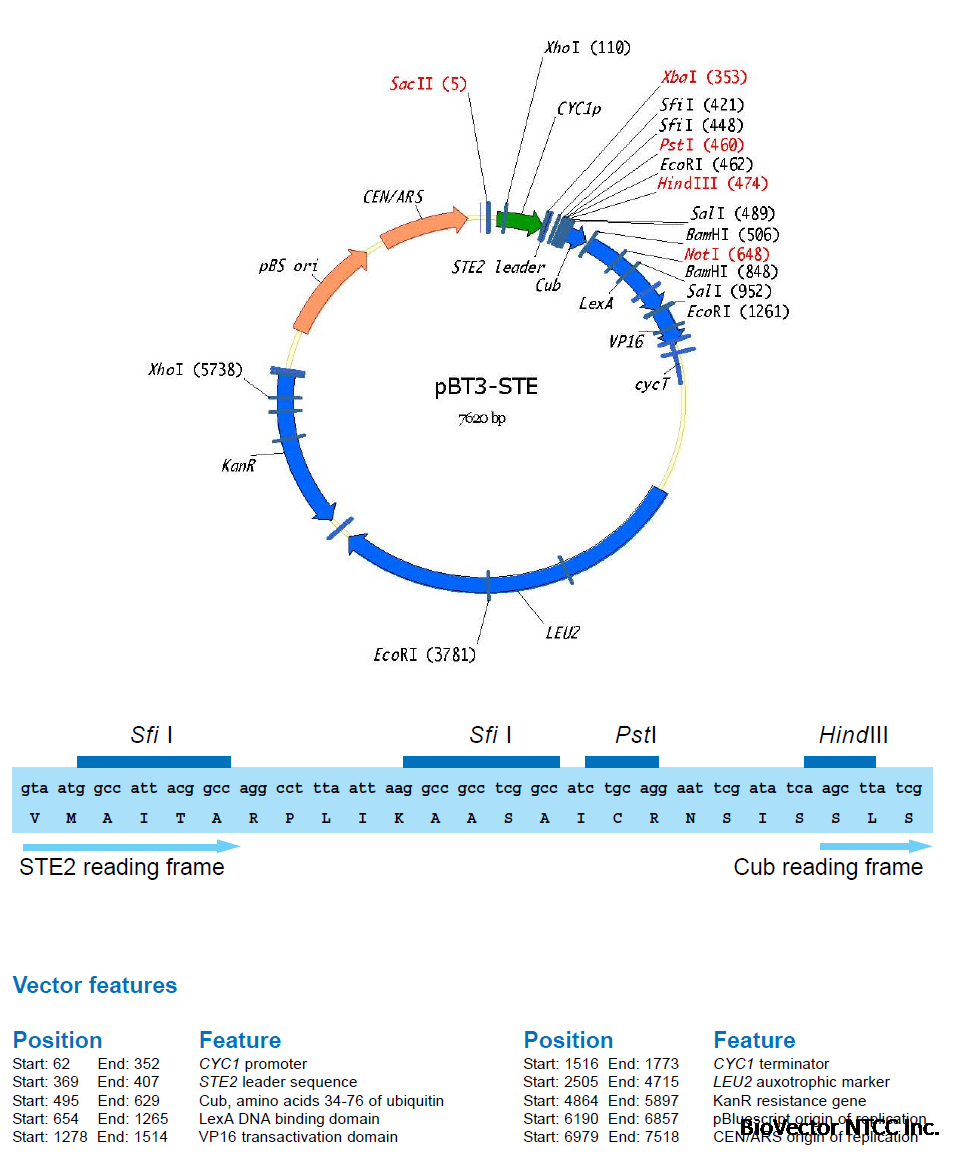
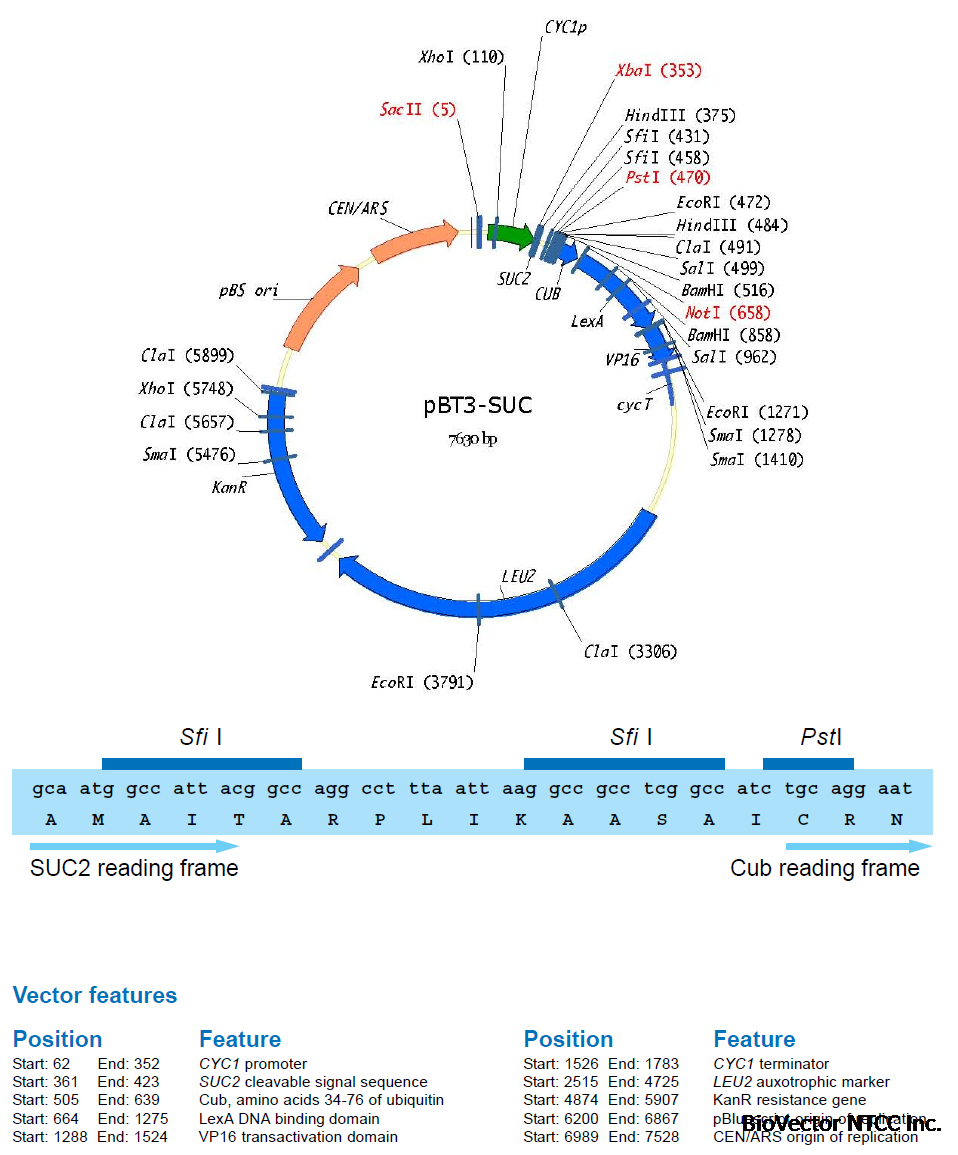
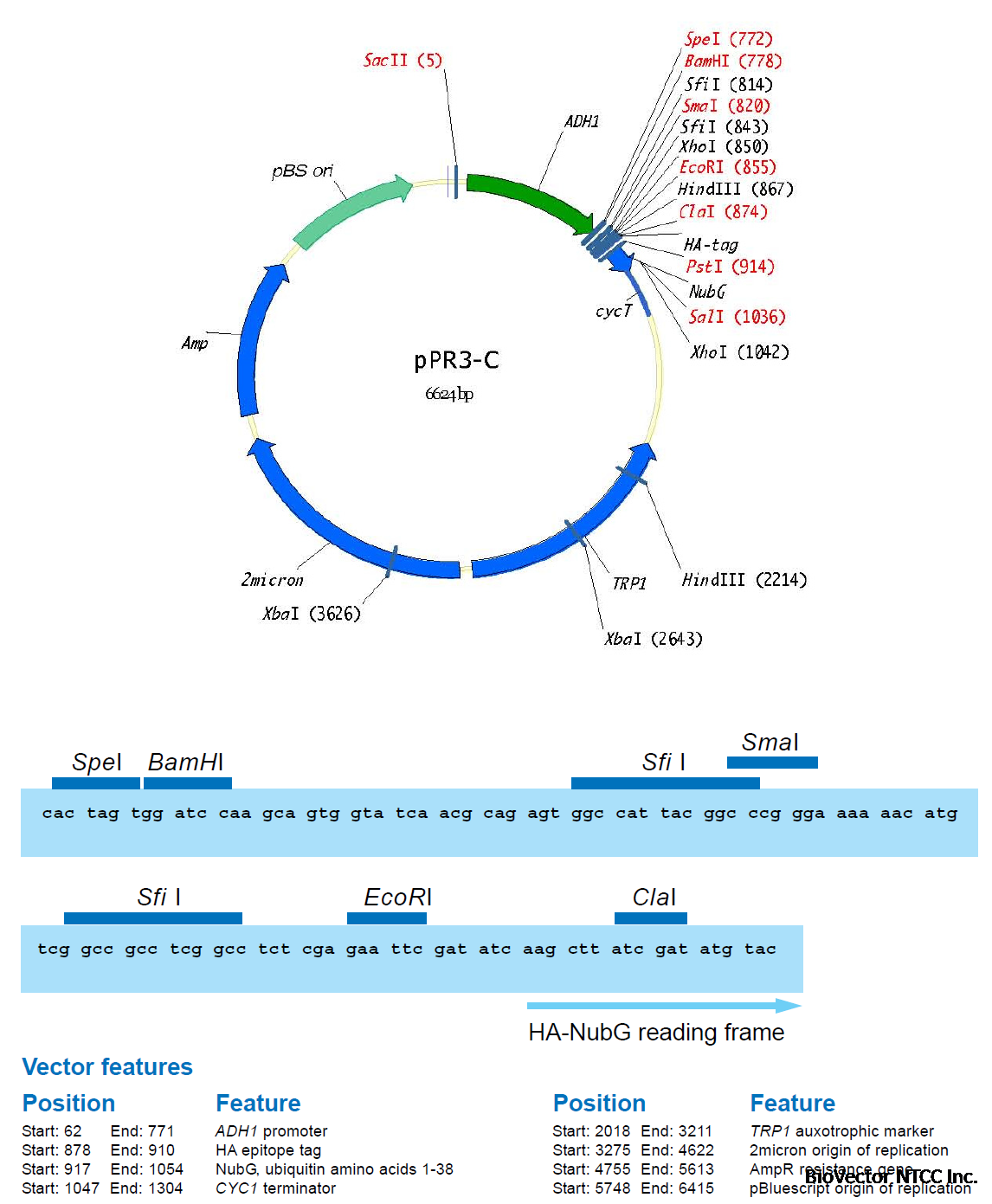
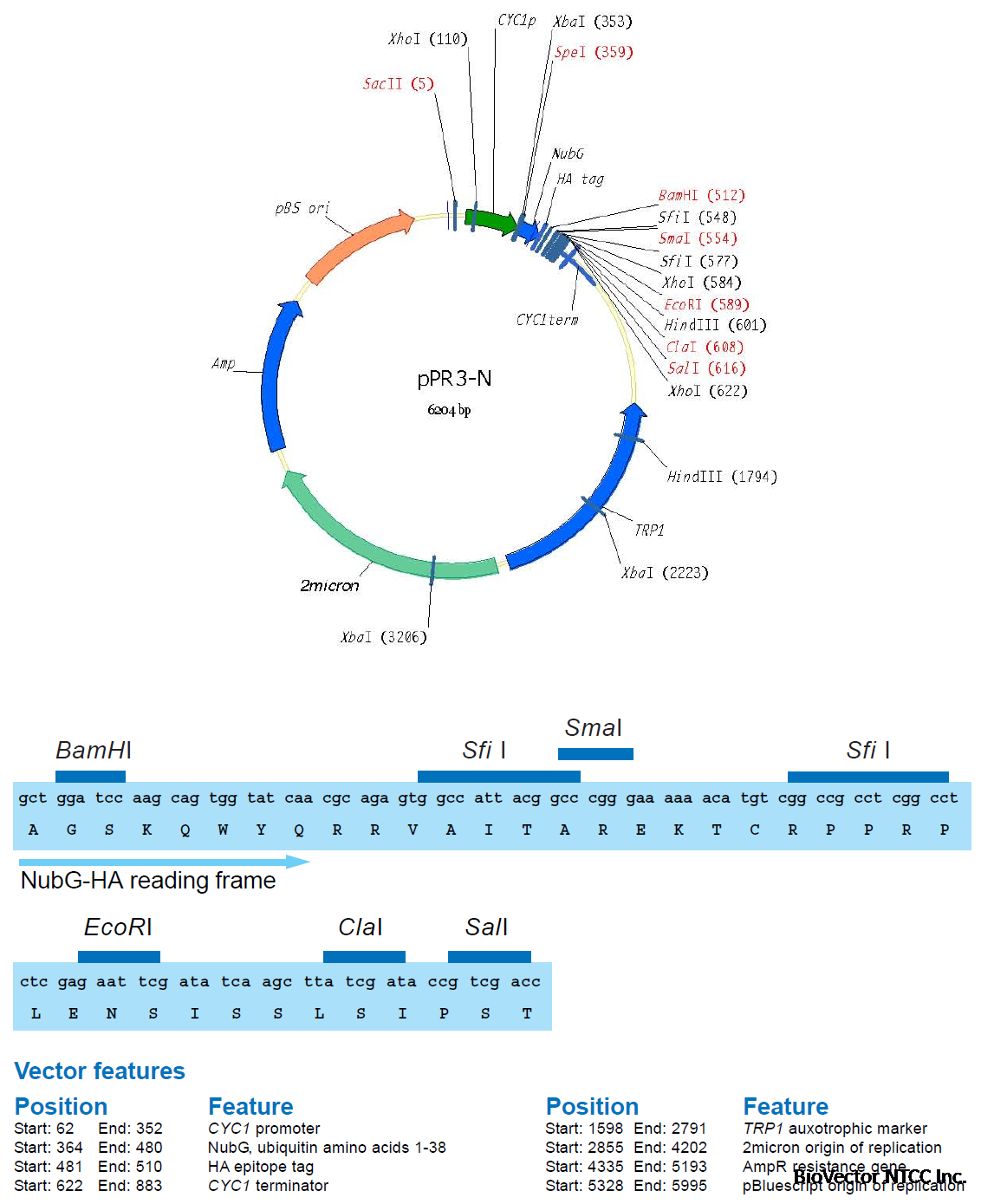
A first membrane protein of interest (the bait) is fused to the C-terminal half of ubiquitin (Cub)
and the artificial transcription factor LexA-VP16 (Figure 4A). A second protein of interest (the
prey) is fused to the mutated N-terminal half of ubiquitin (NubG, Figure 4B). If bait and prey
interact NubG and Cub are forced into close proximity, resulting in the reconstitution of splitubiquitin.
Split-ubiquitin is immediately recognized by UBPs which then cleave the polypeptide
chain between Cub and LexA-VP16. As a result, the artificial transcription factor is released
from the membrane and translocates to the nucleus where it binds to the LexA operators
situated upstream of a reporter gene via its LexA DNA binding domain. The VP16 transactivator
domain then recruits the RNA polymerase II complex to the transcriptional start of the reporter
gene, resulting in its transcriptional activation (Figure 4C). The reporter genes used in the
Y2H membrane protein system are two auxotrophic growth markers (HIS3 and ADE2), whose
activation enables the yeast to grow on defined minimal medium lacking histidine or adenine,
and lacZ, encoding the enzyme β-galactosidase. Thus, the interaction between two proteins
at the membrane of yeast is translated into a transcriptional readout, resulting in growth
of yeast on selective medium and color development in a β-galactosidase assay.
What are the applications of the Y2H membrane protein system?
The Y2H membrane protein kit is intended for the detection and identification of interactions
involving integral membrane proteins and membrane-associated proteins in yeast.
The kit allows you to:
Investigate the interaction between a membrane protein (integral or membraneassociated)
and a membrane protein or soluble protein
Map domains or amino acids which are critical for an interaction
Screen cDNA libraries using a membrane protein as a bait to find novel interacting
proteins
cDNA library screening
Together with the use of NubG-fused cDNA libraries, the Y2H membrane protein system is
capable of identifying novel interaction partners of a given integral membrane protein of
interest. Both cytosolic interaction partners and membrane proteins can be identified in a
screen. cDNA libraries are available in two orientations: NubG-x (expressing fusion proteins
with N-terminal NubG) and x-NubG (expressing fusion proteins with C-terminal NubG). Please
visit www.mobitec.com for premade Y2H membrane protein system cDNA libraries.
Published literature
Below, we have listed some publications citing the use of the Y2H membrane protein system
for investigating pairwise interactions or finding novel protein interactions by screening cDNA
libraries. An updated list of publications can be found at www.mobitec.com
Interactions between defined proteins
Miller, J.P. et al. (2005) Large-scale identification of yeast integral membrane protein
interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102:12123-1218
Yan, A. et al. (2005) Studies of yeast oligosaccharyl transferase subunits using the splitubiquitin
system: topological features and in vivo interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
102:7121-7126
Pandey, S. and Assmann, S.M. (2004) The Arabidopsis putative G protein-coupled receptor
GCR1 interacts with the G protein alpha subunit GPA1 and regulates abscisic acid signaling.
Plant Cell. 16:1616-1632
Library screens
Matsuda, S. et al. (2005) The familial dementia BRI2 gene binds the Alzheimer’s gene APP
and inhibits Abeta production. J. Biol. Chem. 280:28912-28916
Vitale, R. and Buxbaum, J.D. (2004) Use of the split-ubiquitin two-hybrid system to identify
proteins interacting with the Alzheimer proteins APP and LRP. Biol. Bull. 207:167
Wang et al. (2004) The yeast split-ubiquitin membrane protein two-hybrid screen identifies
BAP31 as a regulator of the turnover of endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein tyrosine
phosphatase-like B. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24:276727-78
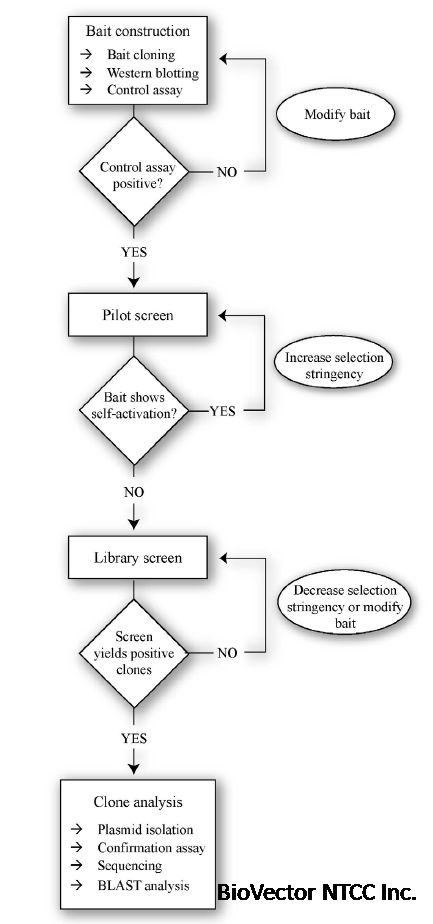
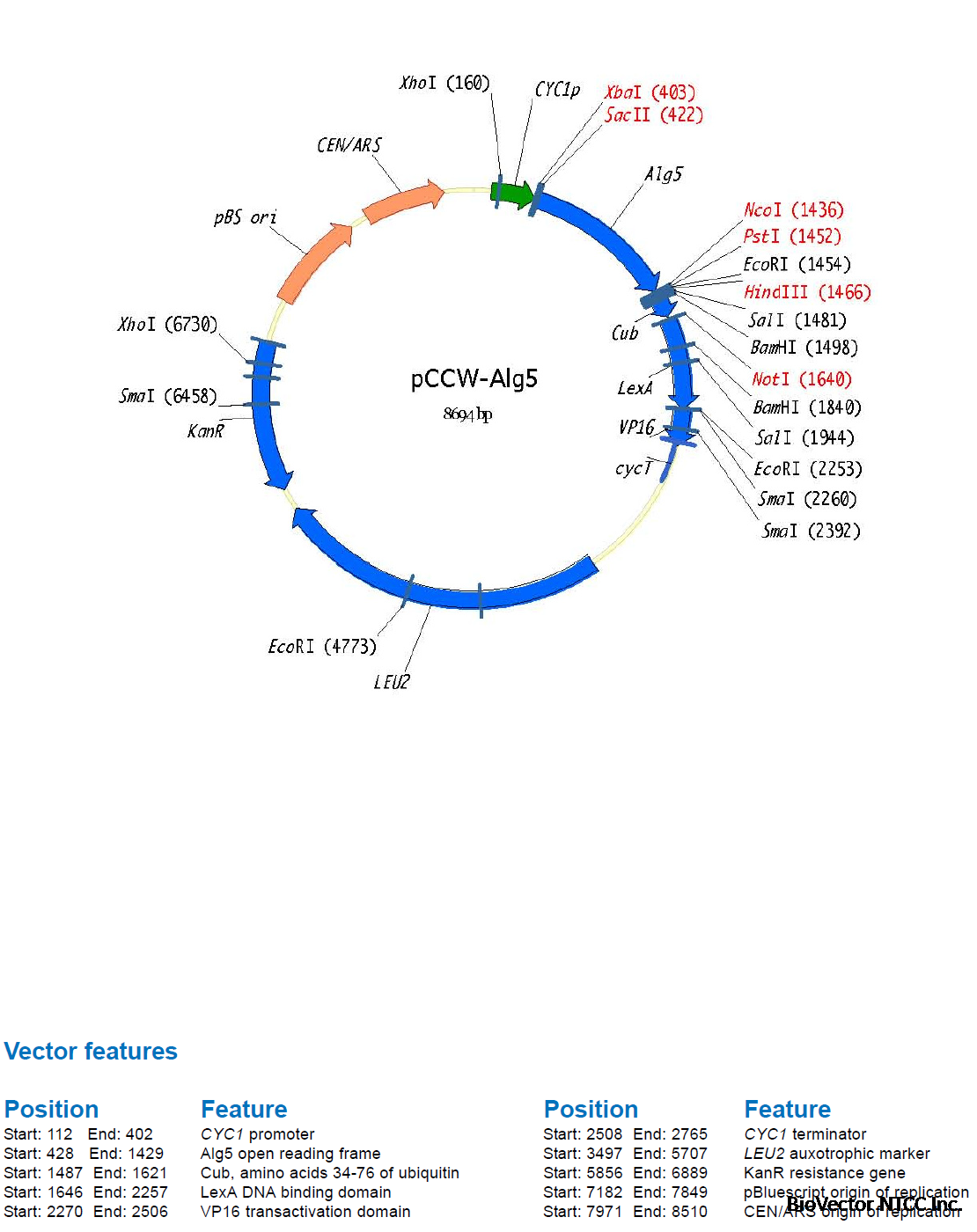
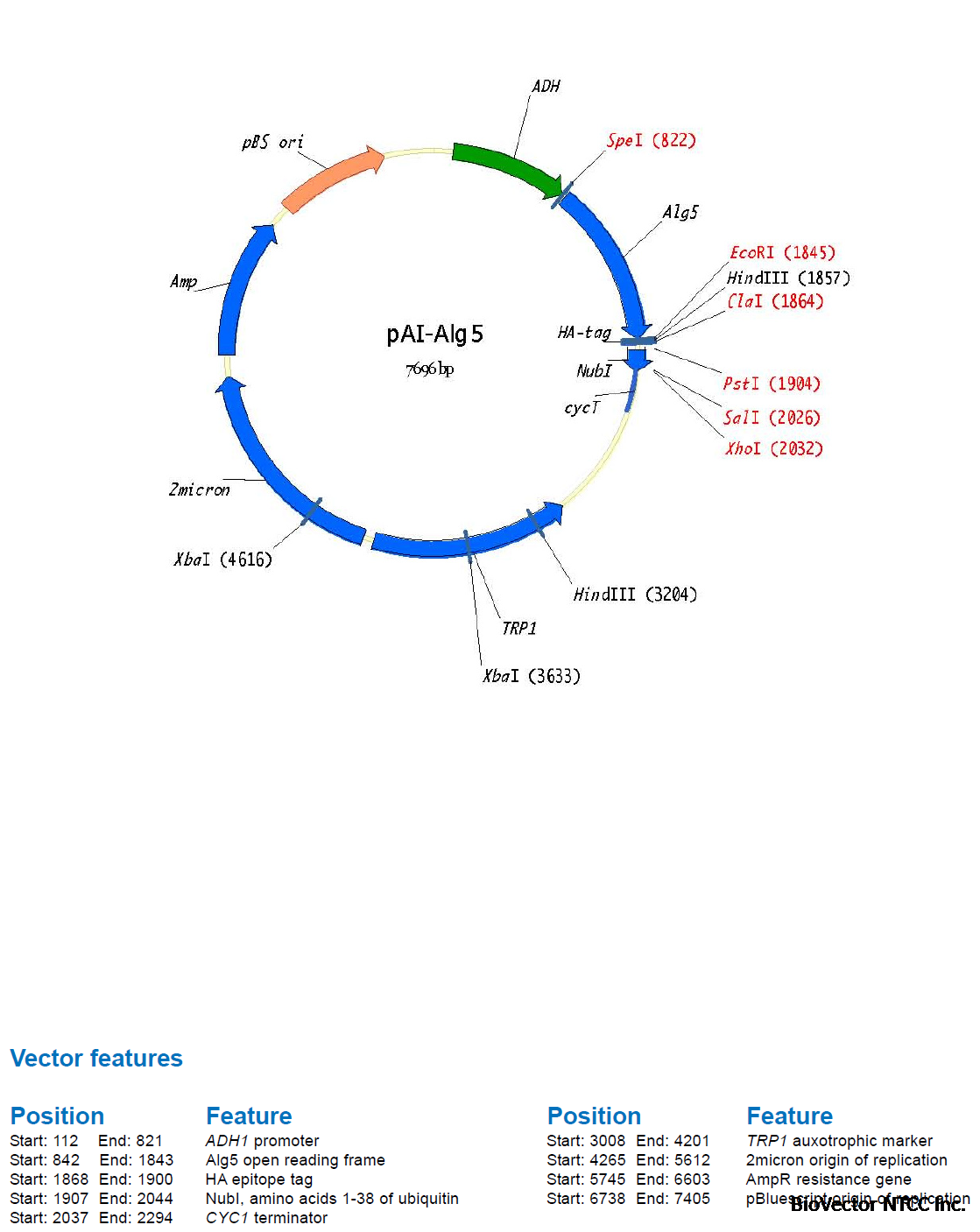
Overview of a Y2H membrane screen
A Y2H membrane screen is divided into three major parts:
Bait construction and expression verification
Library transformation and selection of positive clones
Confirmation of interactors and sequence analysis





- 公告/新闻