- BioVector NTCC典型培养物保藏中心
- 联系人:Dr.Xu, Biovector NTCC Inc.
电话:400-800-2947 工作微信:1843439339 (QQ同号)
邮件:Biovector@163.com
手机:18901268599
地址:北京
- 已注册
pEPI-1非病毒型非整合型自主复制基于S-MAR的稳定表达基因治疗载体-BioVector NTCC Inc.
Nowadays, in most gene therapy trials virus based vectors are used because of their high efficiency. Nevertheless,safety risks like transformation of the cell by viral proteins, insertional mutagenesis, or innate immune reactionscannot be excluded. Basing on the idea of an ideal vector for gene therapy that is highly efficient but lacks thesesafety risks, non viral vectors systems represent an attractive alternative. With the construction of the non viral, S/MAR based vector pEPI at the end of the last century, a first step towards non viral gene therapy has been made.S/MAR based vectors do not contain any viral elements, do not integrate and show stable transgene expression inthe targeted cell or organism. Within the last decade, S/MAR based vectors were further improved and modified,and find now broad application in basic research and also become more and more recognized in gene therapeuticand clinical trials.
pEPI Map:
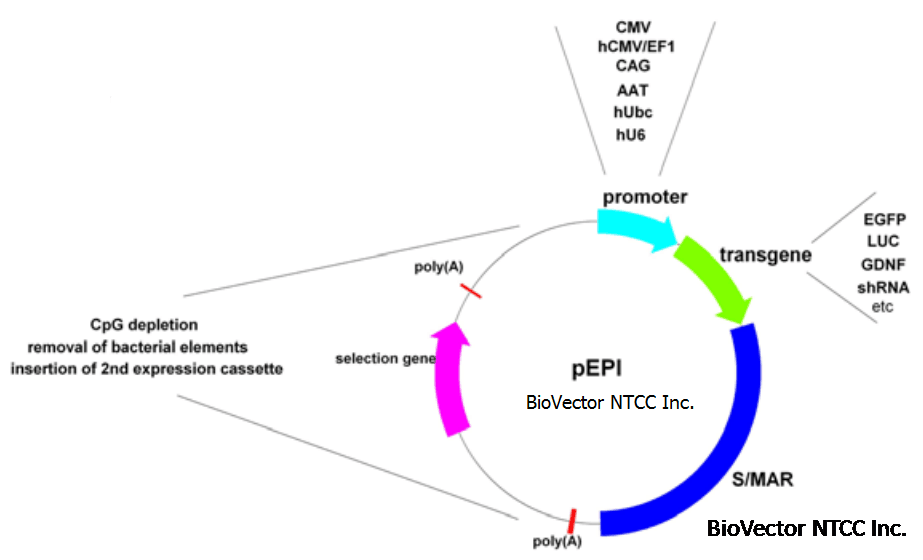
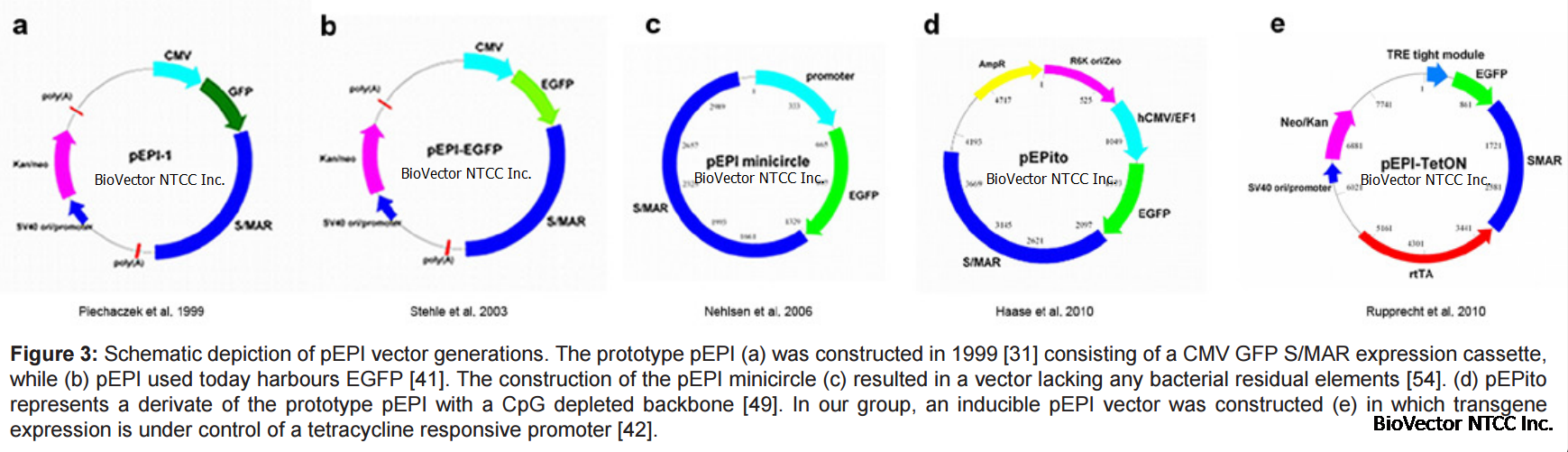
S/MAR sequences are involved in a wide variety of biological processes inwhich compatibility to the nuclear matrix is of importance, includingorigin of replication function [25,26], modulation of gene expression[27], insulator function [28], and long-term maintenance of hightranscription levels by counteracting DNA methylation [29,30]. In thelate 1990 a non viral, episomal, and autonomously replicating plasmidwas constructed in our lab: The S/MAR based vector pEPI replicatesepisomally and is mitotically stable over hundreds of generations in theabsence of selection [31]. During the following years, pEPI attractedmore and more attention. Based on the first prototype, inducible vectorderivates were constructed, pEPI minicircle plasmids were developed,and facing to its potential application in gene therapy approaches, pEPIwas improved for in vitro and in vivo applications. These issues will bediscussed in detail in the following section, pointing out an excitingrole for pEPI in basic research and future gene therapeutic applications(Table 1).
The first vector shown to replicateautonomously in a variety of cell lines and retained in the absenceof selection was the vector pEPI-1. The large T antigen of SV40 wasreplaced by a S/MAR sequence derived from the human β-interferongene cluster [31]. Multiple AATATATTTA elements in this sequenceserve as DNA unwinding elements (DUE) and allow stress-inducedDNA duplex destabilisation of dsDNA [32]. In CHO cells, pEPIreplicates at low copy numbers with 5-10 copies per cell [33] and isstably retained in the absence of selection for basically unlimited time[31]. Episomal maintenance of pEPI was observed in several othercell lines including HeLa, HEK293, and even human primary cells.
In all tested cell lines the vector was mitotically stable in the absenceof selection and occurred in an average copy number below 10 percell [18], indicating a highly efficient replication and segregation. Inestablished cells pEPI is associated with the nuclear matrix via the matrixprotein SAFA and segregation occurs with the host chromosomes viahitchhiking (Figure 1) [34]. Although hitherto data are unsuggestive ofpreferential binding sites of pEPI to certain mitotic chromosomes, itmay be possible that binding of pEPI is restricted to specific sequenceelements [33,35]. Like the cellular genome, pEPI replicates once per cellcycle during early S phase. The origin recognition complex was shownto assemble at various regions of the episome [36], thus behaving as theinitiation zone of genomic origins of replication
- 公告/新闻